At PrintForm we are in constant communication with engineers, mold-makers, CNC machinists, and other self-titled experts in manufacturing. Over the years, our molding experience has grown tremendously and with it, our vocabulary – the collection of which has become our internal molding dictionary of sorts. Instead of keeping it to ourselves, we thought we should share our experience with the world. Below are some of the most commonly used terms (sometimes incorrectly) that frequent our screens on a daily basis.
What did we miss? We challenge you to send us your team’s most used terminology: email blog@printformtech.com
Annealing
The process of relieving the internal stresses of molded plastic components by heating to a predetermined temperature, maintaining this temperature for a predetermined length of time, and slowly cooling the part.
.
Blowing & Foaming Agents
Additives for plastics or rubbers that generate inert gases within the resin matrix when heated. The resulting part construction will contain a cellular structure.

Cavity
Refers to the upper half of the injection mold usually the show (outer) surface of the finished product and is mainly concave.
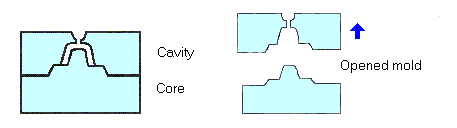
Core
Refers to the side of the tool where the plastic part is injected from; also known as the bottom half of the mold.

Cycle Time
The time required by an injection molding system to mold a part and return to its original position/state.

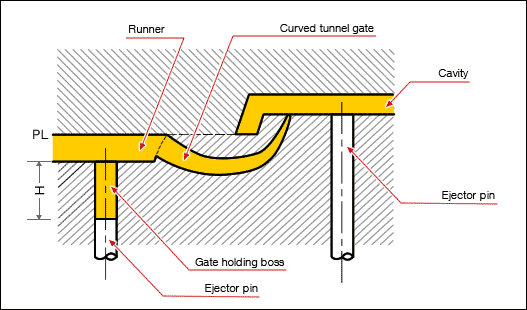
Gate
Area where the plastic enters into the cavity of the mold, could be one or more gate locations.
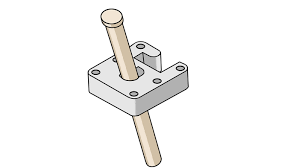
Hand Load
Aluminum or steel feature, CNC machined by the tool maker, in a mold used to accommodate designed in undercuts in molded parts. They are manually removed from the mold during the part ejection process.

Heel
The portion of an automatic/mechanical injection mold that maintains the position of the slide when the molding machine is closed on the mold.
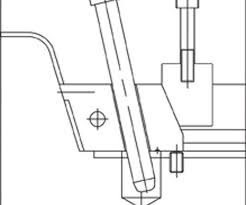
Horn (Angle) Pin
Pin used to actuate the slide in an automatic injection mold system.
Runner
A channel cut into an injection mold tool, where molten plastic travels from the injection molding machine, through the sprue, through the runner and then through the gate ultimately filling the part cavity.

Shear
Refers to when plastic enters into the mold and the melt is maintained by friction produced by speed and pressure. Too much shear can cause the plastic material to burn, too little can cause the material to freeze off causing short shot and resulting voids.

Side Action
Term used for slides and/or hand pulls used in the injection mold build process. Necessity of which is determined by the complexity of the end part.

Vestige
Material protruding from the gate area after gate runner has been removed from the injection molded part. This vestige is manually or mechanically trimmed by the molding machine operator.














